| (insert your NIE or newspaper logo here) | Weekly Online LessonOnline Lesson ArchiveGrade Level: 6-9
|
Spotlight On Stem Cells
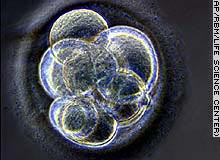 Human embryos made in laboratories by in vitro fertilization have
served as miracles to many infertile women, allowing them to become
impregnated and have children.
Human embryos made in laboratories by in vitro fertilization have
served as miracles to many infertile women, allowing them to become
impregnated and have children.
In the past, some of these embryos have also been used in medical research. For example, scientists have extracted what are called "stem cells" from embryos, a procedure which destroys the embryos. The stem cells are then used in research to help diabetics and people with Parkinson's disease and other debilitating conditions.
In 2001, President George W. Bush banned federal funding of stem cell research that used viable human embryos, citing that the procedure essentially takes a human life and therefore shouldn't be condoned by the government. Any embryo stem cell lines already created by the procedure could still be used for research purposes.
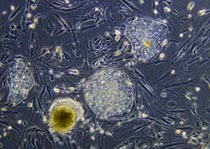 But on Tuesday, May 24, 2005, the U.S. House of Representatives defied
the president by passing a bill called, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement
Act that would again allow federal funding of stem cell research using
human embryos.
But on Tuesday, May 24, 2005, the U.S. House of Representatives defied
the president by passing a bill called, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement
Act that would again allow federal funding of stem cell research using
human embryos.
The bill was created based on expert testimony that the stem cell lines OK'd by the President in 2001 are mostly contaminated or unusable.
Soon after passing the Enhancement Act, the House passed another bill, called the Stem Cell Therapeutic and Research Act. Unlike the former, this bill allows federal funding of research that uses stem cells taken from umbilical cord blood and adults instead of embryos.
So why don't researchers only use these alternative stem cell sources instead of taking some from embryos?
During this week's lesson, you'll discover the differences in how stem cells develop and function depending on their source. You'll also learn about how scientists are using stem cells - from a variety of sources - to study how they can be used to cure certain illnesses and afflictions.
A Study of Stem Cells
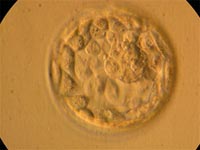 Start your lesson with an introduction to Human
Embryonic Stem Cells. After reading the overview, Click to
view animation.
Start your lesson with an introduction to Human
Embryonic Stem Cells. After reading the overview, Click to
view animation.
Choose the Narrated version if your system has speakers. Choose the Step-Through version if it doesn't.
What are the two key features of embryonic stem cells? How exactly could this type of stem cell research be used to treat diabetics?
Now let's really put Stem Cells in the Spotlight, with an in-depth study at The University of Utah's Genetic Science Learning Center.
Begin with a closer look at What is a stem cell?
Click the bottom right arrow to move forward to the presentation's next section. Click View Animation after reading the text in each section. When you arrive at the Differentiation Booth, dial-up each of the directory listings except for 6 - Done.
What happens to Stem Cell Guy when he receives a signal? What exactly does "differentiate" mean? What is the process Stem Cell Guy has to go through to become each type of tissue?
After you've gone through the last cell type, instead of returning to the booth, choose to learn about the different types of stem cells. Make sure to review the Quiz Clues as you play the animation, and Take the Lab Coat Quiz at the end.
 What are the two types of cells in a blastocyst? What functions
do stems cells in a fetus perform? How do the stem cells from different
sources compare to one another?
What are the two types of cells in a blastocyst? What functions
do stems cells in a fetus perform? How do the stem cells from different
sources compare to one another?
After the quiz, find out why researchers study stem cells in the lab. What is the ultimate goal of stem cell therapy?
Next, review some Stem Cell Therapies.
Read the introduction, then go through the sequence of steps, from Step 1: Define the Problem through Step 5: Make the Transplanted Stem Cells Perform.
What factors determined which type of stem cell was the best one to use? How were the stem cells matched to the recipient? How were the stem cells delivered to the right place in the patient? What happens after the stem cells are transplanted?
 What
risks are involved in this procedure? How can doctors determine whether
the transplant has helped or not?
What
risks are involved in this procedure? How can doctors determine whether
the transplant has helped or not?
Now, compare Stem Cell Therapies Today with Stem Cell Therapies in the Future.
Then, find out what steps are taken in Creating Stem Cells for Research and What Are Some Issues In Stem Cell Research?
How might your views on the issues be different if you lived with different circumstances or were raised in a household with different social or moral values? What if you were a politician or a scientist?
Lastly, take the online survey of What You Think. How do your answers compare with others who completed the survey?
Newspaper Activities
Browse current issues of The Salt Lake Tribune to find stories related to stem cell research. Did your state's federal representatives vote for or against each bill? Which senators are debating for and against the two related bills? Do your state's senators say which way they will vote on the bills? What is President Bush saying or doing in response to the debate over the two bills? In what ways are scientists, special interest groups, or members of the general public responding or contributing to the debate? What are the most important points being made on each side of the debate? Which points are based mostly on personal moral values? If you find news about another country developing stem cell research, how does the research, the government's role, or political or public debate over the research compare to that in the United States?
© Copyright 2005
Learners Online, Inc.
