| (insert your NIE or newspaper logo here) |
Weekly Online LessonOnline Lesson ArchiveGrade Level: 7-12
|
Nuked Up
 Can you imagine shopping at Wal-Mart to load up with all the nuclear weapons you could afford?
Can you imagine shopping at Wal-Mart to load up with all the nuclear weapons you could afford?
The head of the United Nations' International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) announced Friday, January 23, 2004, that's just about what's happening around the world, thanks to the black market trade of nuclear-related materials, design blueprints, and equipment.
The revelation came as agency officials toured Libya, one link in this illegal market's chain.
Following the tour, Mohamed M. ElBaradei, director-general of the IAEA, concluded that, "When you see things being designed in one country, manufactured in two or three others, shipped to a fourth, redirected to a fifth, that means there's lots of offices all over the world. The sophistication of the process, frankly, has surpassed my expectations."
Also over the last week, the U.S. government said that it may move to strengthen the nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), to prevent countries from legally acquiring nuclear components that could be used to boost weapons programs. While it's important to provide nations with nuclear energy to generate electricity, the potential rule change would deny them the right to manufacture, store or reprocess nuclear fuel — a key component of nuclear bombs.
The NPT is a landmark international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, and to further the goal of achieving nuclear disarmament. The U.S. is one of the world's five declared nuclear weapon states, which have agreed to not use these weapons. Instead, they are charged with helping the non-nuclear weapon states develop peaceful uses of nuclear energy, as long as those nations agree not to transform those resources into weapons.
About 187 parties have joined the treaty since 1970, but it has been clear that some NPT signatories — like Iran, Libya and North Korea — used the agreement to get themselves closer to nuclear weapons production.
 Meanwhile, some experts believe the Bush administration may push to restart nuclear weapons testing at the Nevada Test Site — about an hour northwest of Las Vegas and larger than the state of Rhode Island.
Meanwhile, some experts believe the Bush administration may push to restart nuclear weapons testing at the Nevada Test Site — about an hour northwest of Las Vegas and larger than the state of Rhode Island.
Historically, the United States government detonated 1,039 nuclear devices — more than any other nation. These explosions occurred at several different sites, including the Nevada site, between 1945 and 1992, until such testing was banned.
Nuclear weapons, wielded by friend or foe, are a concern for everyone, because the direct and indirect effects of their use are devastating and horrific. The immediate blast of the atomic bomb killed over 150,000 residents of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan at the end of World War II. The lingering radioactivity from those bombs, as well as those exploded at test sites, has degraded the health of thousands more and severely damaged the environment in those areas.
To understand why nuclear devices are so lethal and powerful, this week's lesson will show you how nuclear reactions work and how they're harnessed for destruction. You'll also uncover the history of the atomic age, and find out who's got nukes today.
An Atom's Power
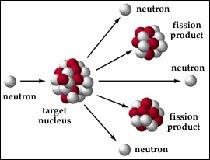 Your tour begins at the Atomic Archive for a zoom-lens view onto the Science behind nuclear weapons.
Your tour begins at the Atomic Archive for a zoom-lens view onto the Science behind nuclear weapons.
First check out Nuclear Fission. Click Next to move through the section's pages, and play the QuickTime movies in the Related Media boxes.
So what happens to the "missing" mass? What happens during a chain reaction? What's the importance of producing controlled nuclear fission? Why do scientists use Uranium and Plutonium? How do the spontaneous fission rates of plutonium and uranium compare?
Next, find out how the Little Boy is equipped, and check out its Time of Reaction. How does its design compare to the Fat Man? How exactly does the Detonation Sequence work, and why were explosive charges used?
Your next exploration takes you into Nuclear Fusion. Make sure to find out The Basics, The Secret, the Schematic.
How does The Neutron Bomb design compare with the Little Boy and Fat Man? How is nuclear fusion different from nuclear fission in their process and effects?
Deeper Than A Scar
 You've looked closely at the process of nuclear explosions, now look at the Effects of Nuclear Weapons, including The Effects of Radiation on the Human Body and the Levels of Radiation on the Human Body.
You've looked closely at the process of nuclear explosions, now look at the Effects of Nuclear Weapons, including The Effects of Radiation on the Human Body and the Levels of Radiation on the Human Body.
What are the health effects of even the smallest dose of radiation? Which parts of the body are affected by a level of about 200 rems?
Next, take a different view by visiting the New York Example. Read the introduction explaining why they chose to maintain this section after the September 11 attacks, then move on to the time and place of the fictitious bomb detonation at the foot of the Empire State Building.
Move out from ground zero and through the time sequence: 1 second after detonation, 4 seconds, 6 seconds, 10 seconds, 16 seconds, and the Long-Term Fallout Pattern.
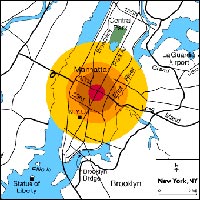 Finish up the section with the Recovery and Summary.
Finish up the section with the Recovery and Summary.
How quickly did the blast wave move? How did the force and the heat contribute to the casualty levels in the different pressure rings? What were the fallout effects, and how big was the total area affected by the blast?
Before leaving Atomic Archive, browse the Media section. Take a look at some of the historical Photographs, view some of the Videos, and scrutinize the Maps.
What components and effects of nuclear explosions are predictable and controllable? Which ones aren't? How do environmental factors, such as wind and topography, affect the results? What were some long-term consequences suffered by survivors of weapons testing?
Our Nuclear Legacy
 So what led up to the United States unleashing such a devastating force on Japan in 1945?
So what led up to the United States unleashing such a devastating force on Japan in 1945?
To discover the answer, follow The Race To Build The Atomic Bomb, created by the Contra Costa County Office of Education.
First, read the introduction — who were the three competing nations? Then open the US/Eng. Timeline, and Click for Timeline to scroll along.
How did advancements in science and technology support and guide political action? In what ways did the government support and guide science and technology?
Now take a look at the Competition -- Germany & Japan. How did their advancements in nuclear weaponry compare to that of the U.S.?
 Also read about the Exodus of Scientist and Those Responsible. How may the war have turned out differently if Adolf Hitler's actions, attitude, and allies had not prompted the scientists to flee their homelands? What roles did the different types of people play in the development of nuclear weapons?
Also read about the Exodus of Scientist and Those Responsible. How may the war have turned out differently if Adolf Hitler's actions, attitude, and allies had not prompted the scientists to flee their homelands? What roles did the different types of people play in the development of nuclear weapons?
Lastly for this week's lesson, visit two interactives. First, go to the PBS site, Avoiding Armageddon and Learn the Facts by launching the WMD Primer (Flash Player required). Click on Map It for Nuclear (the color red) to see which nations have or may have nuclear weapons. Then click on each of those nation's names to read their weapons statistics.
Secondly, visit the Global Security Institute's Resources section, and watch their QuickTime movie about the potential failure of Missile Defense Countermeasures against incoming nuclear warheads.
Do you think the United States should restart nuclear weapons testing? What are the pros and cons of doing so? What could happen if the U.S. and the United Nations fail to curb the black market nuclear weapons trade?
Newspaper Activities
Browse current issues of Targetnewspaper, and look for stories about nuclear weapons. Has intelligence uncovered further evidence of black market trading? Has the Bush administration come forward with a proposal to close the Non-Proliferation Treaty's current loophole? If so, how have North Korea, Iran, and other nations reacted? If the American government is pushing to lift the ban on nuclear weapons testing, how are American citizens reacting? How are citizens of other nations reacting?
© Copyright 2004
Learners Online, Inc.
